Study of Semiconductors
Heating of specimens under vacuum in a quartz tube
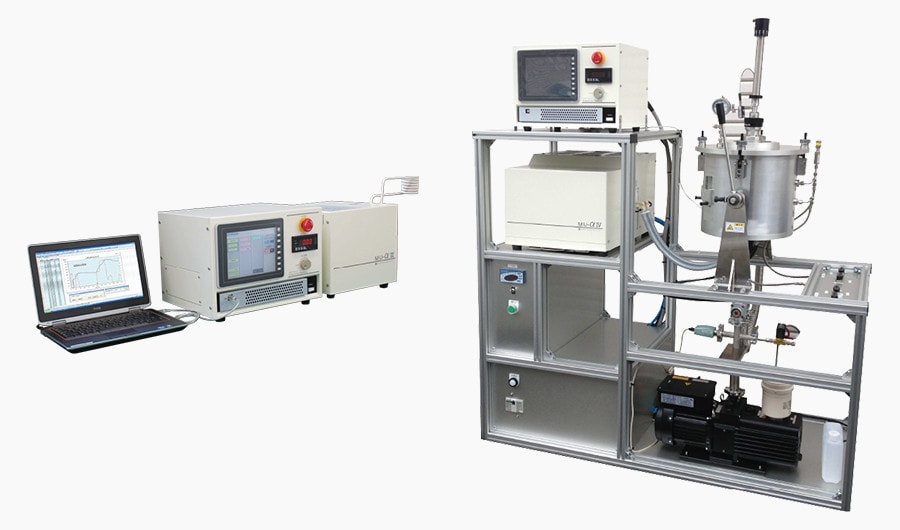

The high frequency induction heating system MU-α series is made compact in a personal-computer size into which a conventional large-sized and expensive heating system is being transformed. This space-saving and highly functional system MU-α is to be used for study of physical properties, study of semiconductors, and sample preparation.
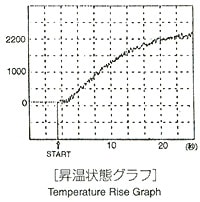
When using a crucible made of a material having a high melting point such as carbon, tungsten, or molybdenum, operations can be executed at a maximum temperature of about 2,200°C.
(Ex.) Heating carbon in a vacuum using carbon fiber as a thermally insulating light blocking material
Manufacturer : SK Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.


Heating of specimens under vacuum in a quartz tube
Heating of liquids, powders or gases by placing a heater (carbon honeycomb, metallic ring or the like) in the fluid passage.
A glass specimen is locally heated,molten,and welded to the electrode such that the inside gas is encapsulated.
Heating of specimens, for example, a SUS round rod of 20φ, to 600°C in about 30 sec.
Direct heating of metallic specimens. One of a variety of crucibles is to be selected according to heat resistance and reactivity.
With the use of a vacuum/gas replacement unit (optional), just the atmosphere around specimens can be controlled.
Heating and melting pure silicon, glass, ash, or other specimens by high-frequency induction rather than direct heating.
Study of battery materials or preparation of alloys from metals of differing melting or boiling points.